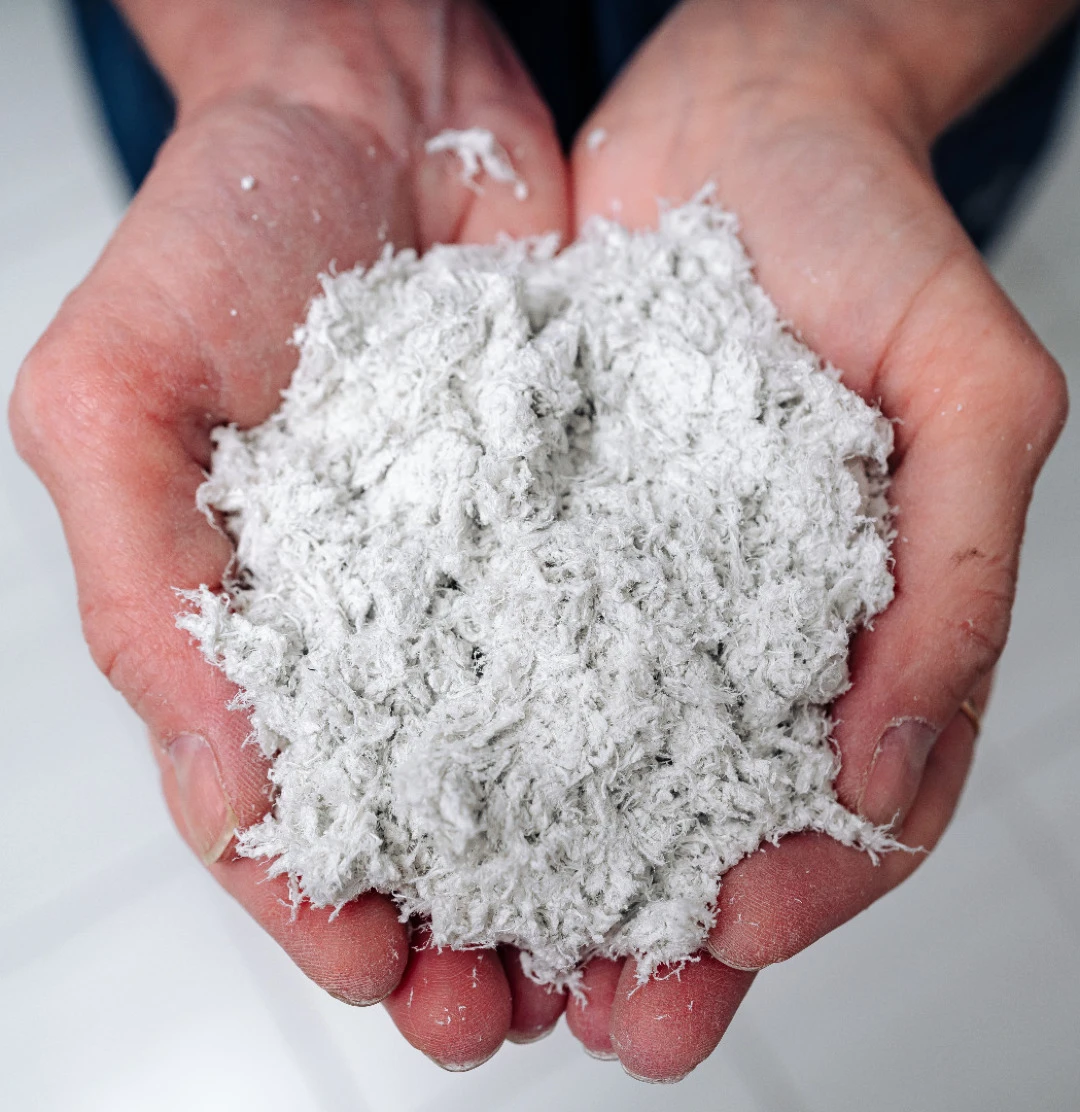
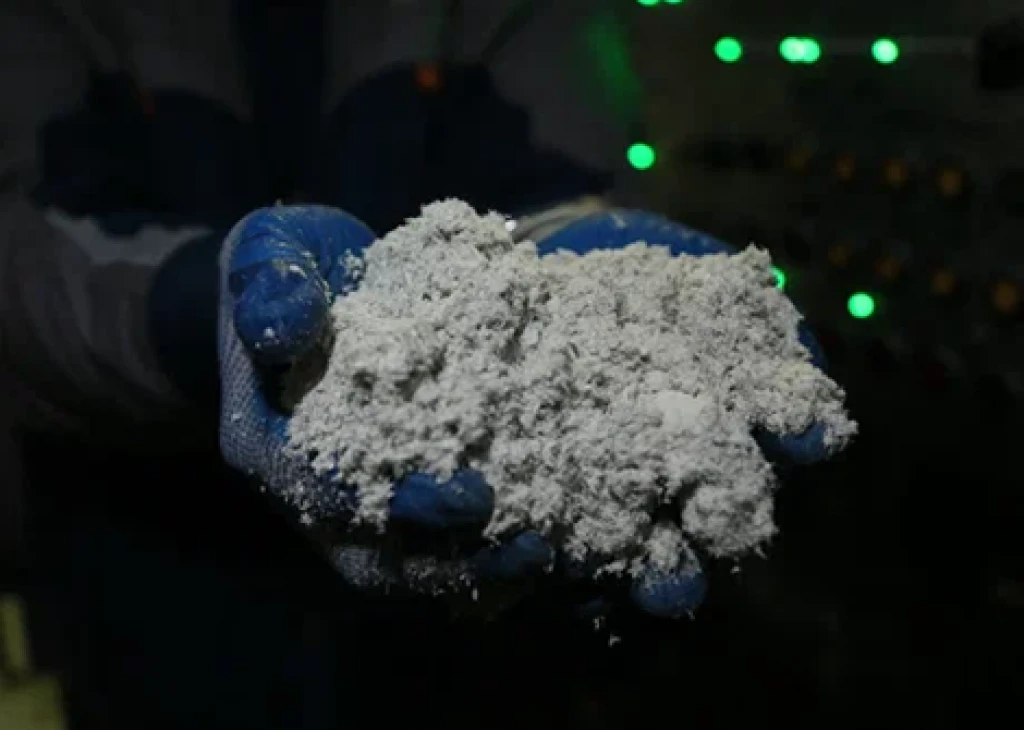
Chrysotile asbestos, or "white asbestos," belongs to a group of natural minerals commercially known as "asbestos."
It is part of the serpentine group and structurally classified as a layered silicate. Chrysotile asbestos has the chemical formula 3MgO•2SiO₂•2H₂O, representing a magnesium hydrosilicate naturally found in the form of crystals composed of hollow fibril tubes with a diameter of 2.6•10⁻⁵ mm and a length of up to 2–3 cm.
The mineral can split into extremely fine chrysotile fibers, with a thickness of up to 0.5 μm.

Safe
 Density over 3000 MPa
Density over 3000 MPa
Eco-friendly
 Does not harm nature
Does not harm nature
Anti-corrosion
 Resistant to corrosion
Resistant to corrosion
Durable
 Stronger than steel
Stronger than steel
Fire-resistant
 Thermal insulating and non-conductive
Thermal insulating and non-conductive
Moisture resistance
 Water-resistant and waterproof
Water-resistant and waterproof
Absorbent
 Absorbent
Absorbent

Asbestos-cement sheets, foam concrete
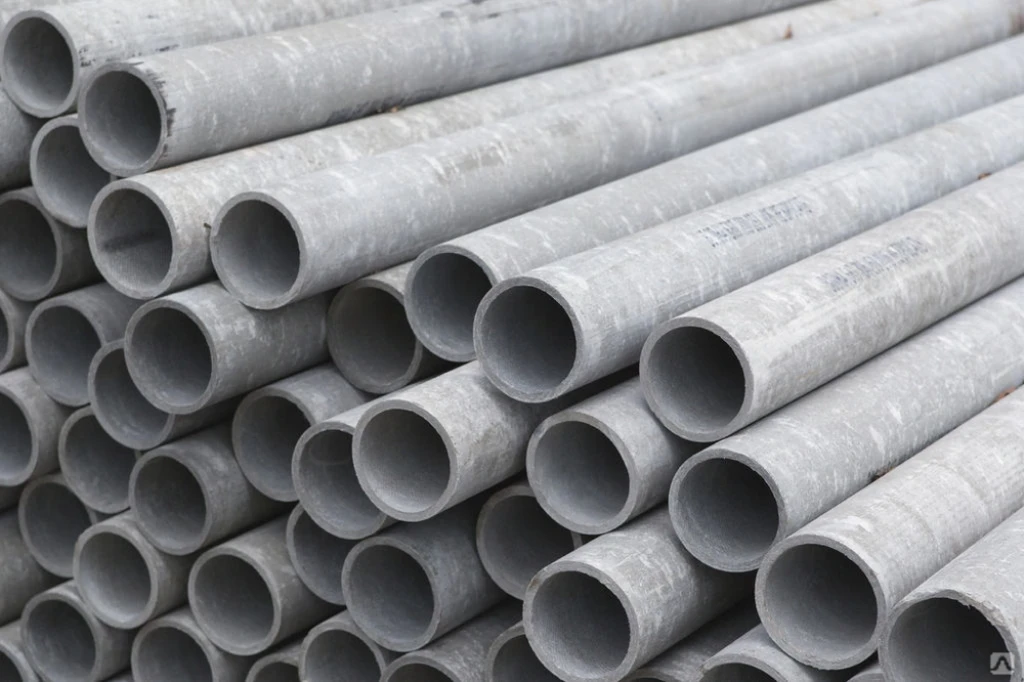

Pressure and non-pressure pipes
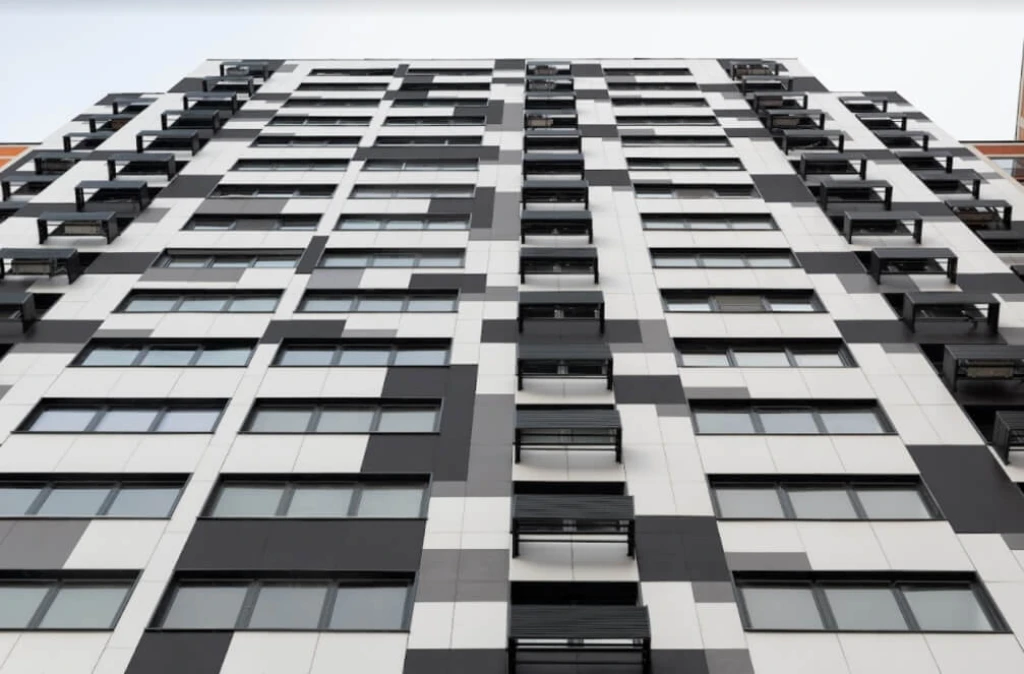

Flat or corrugated sheets
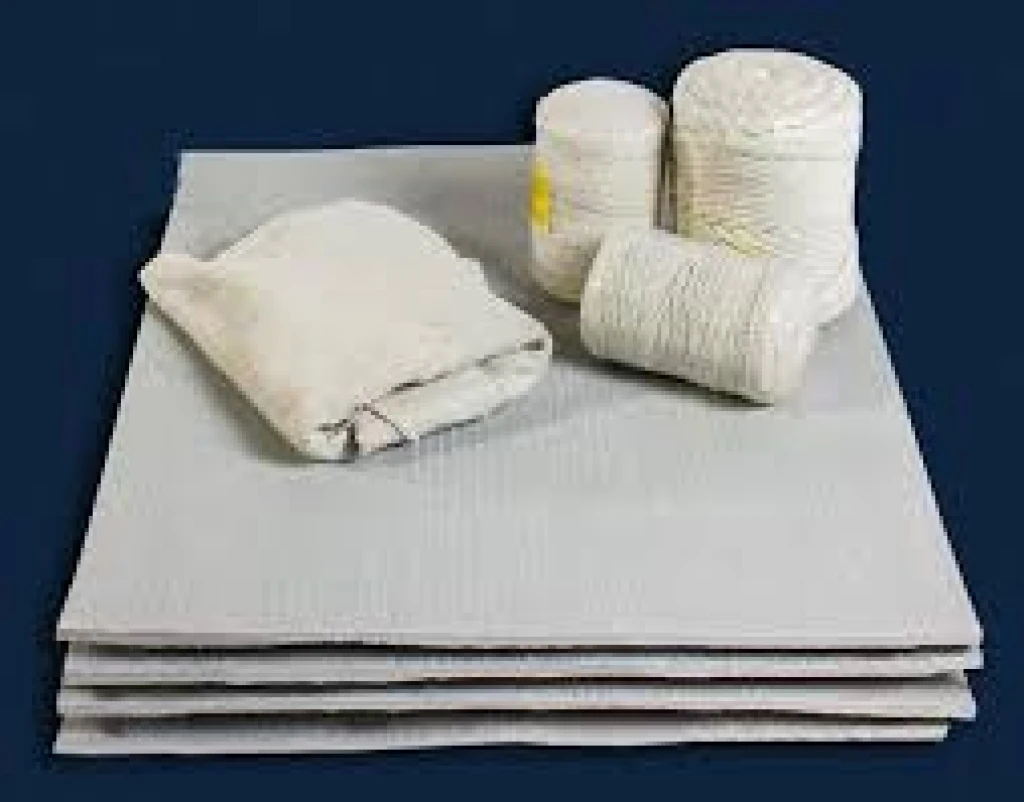

Fabrics, cords, boards, filters, and more
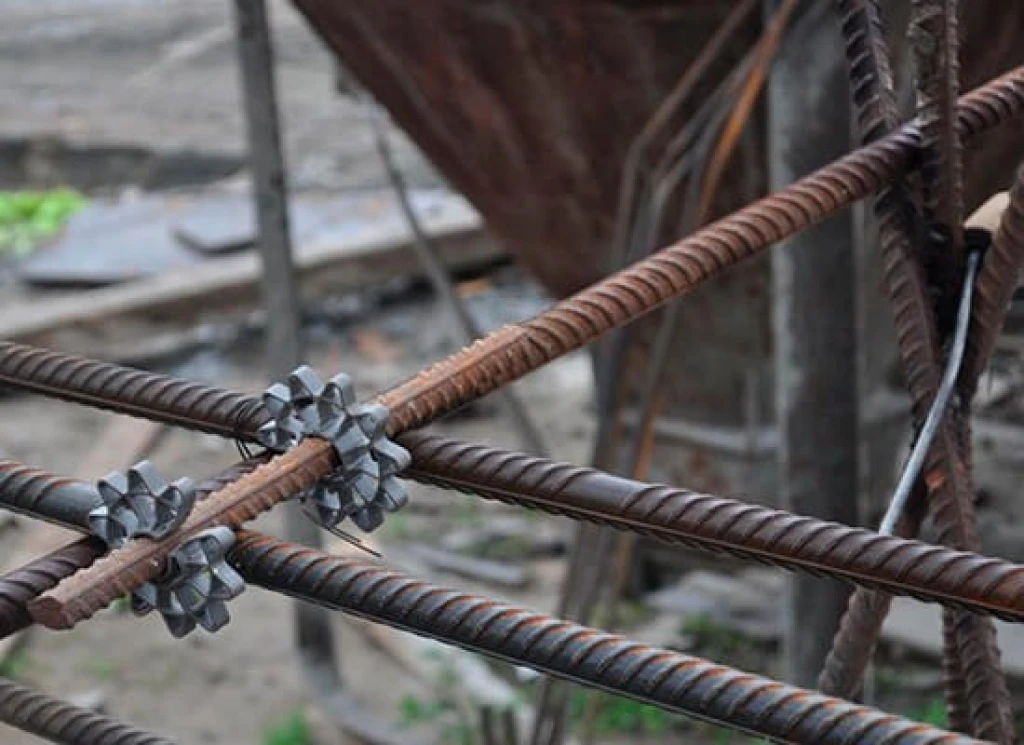

Tunnel lining and sealant components
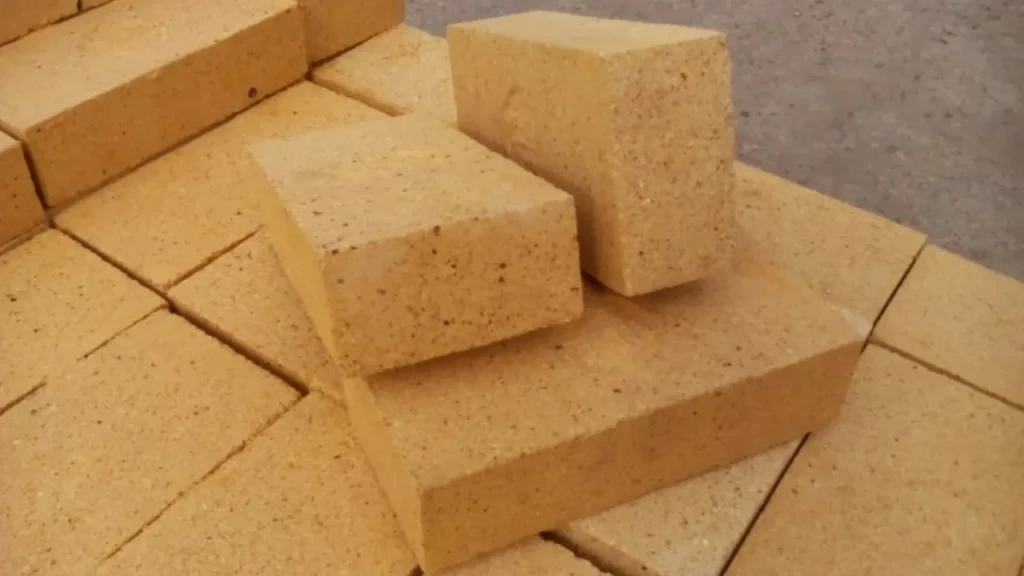

Bricks
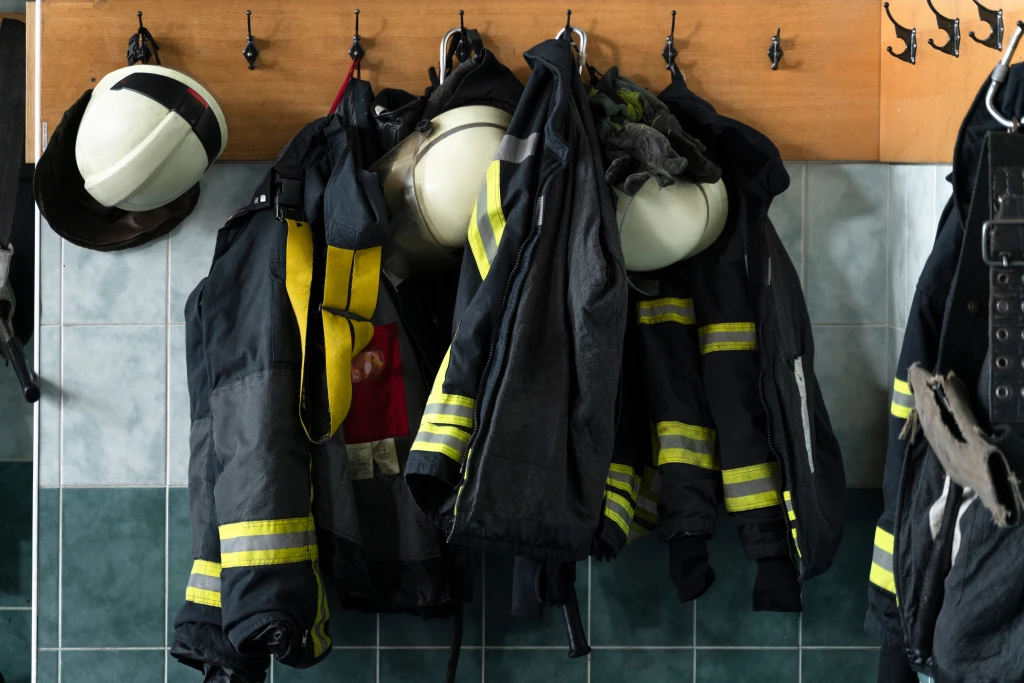

For occupations with exposure risk
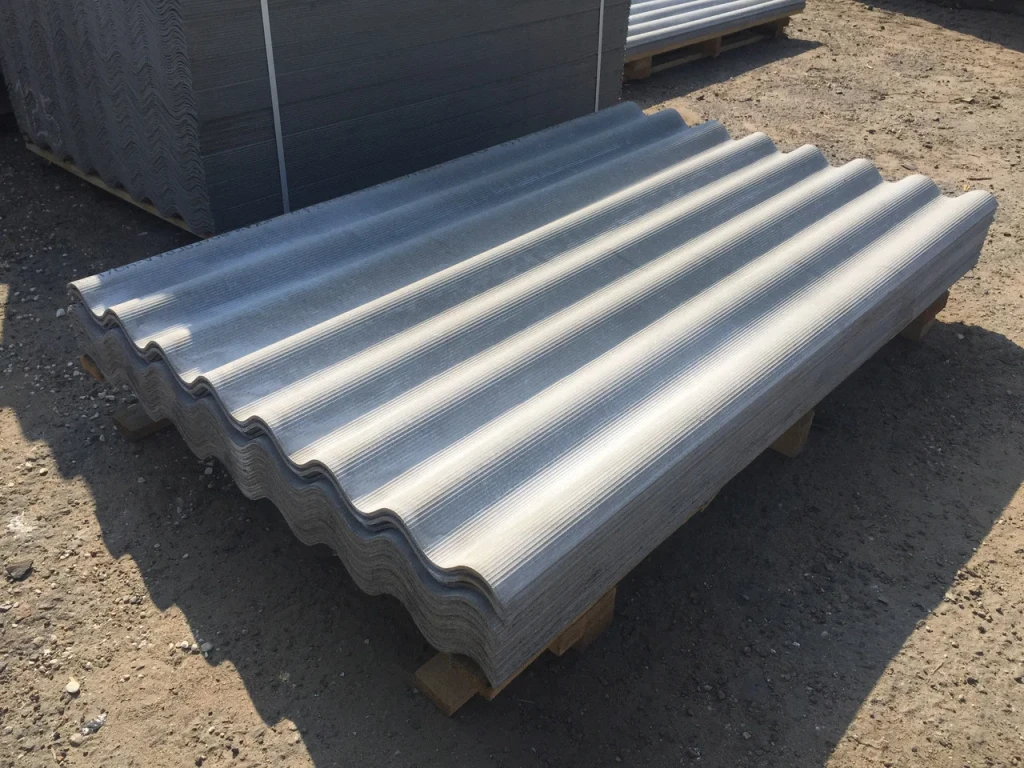

Slate, various types of pipes
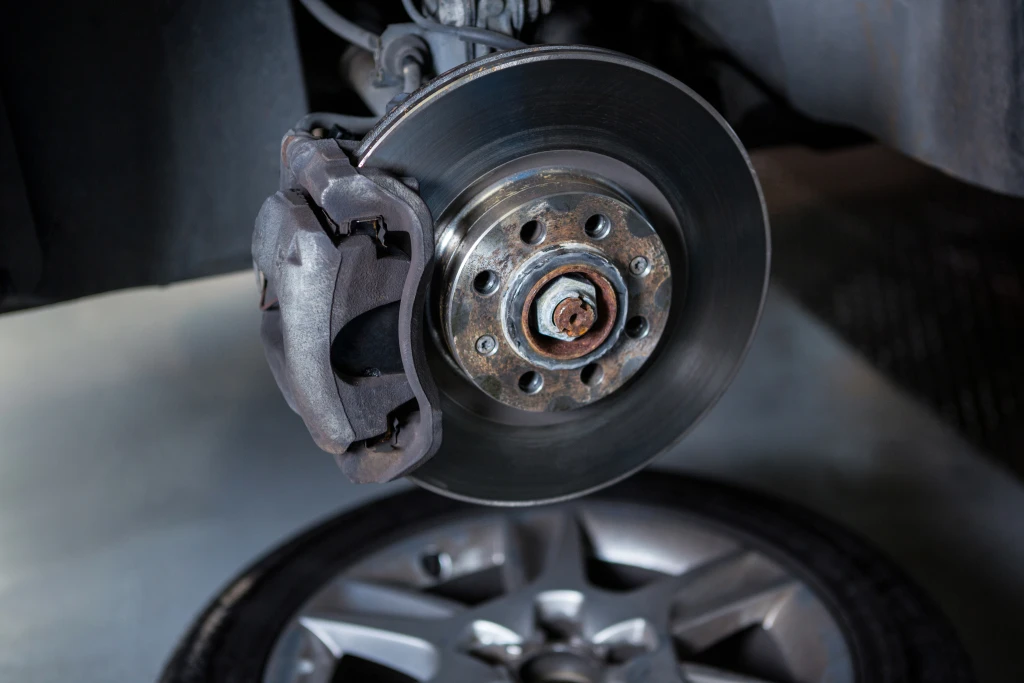

Brake pads, clutch facings, and more
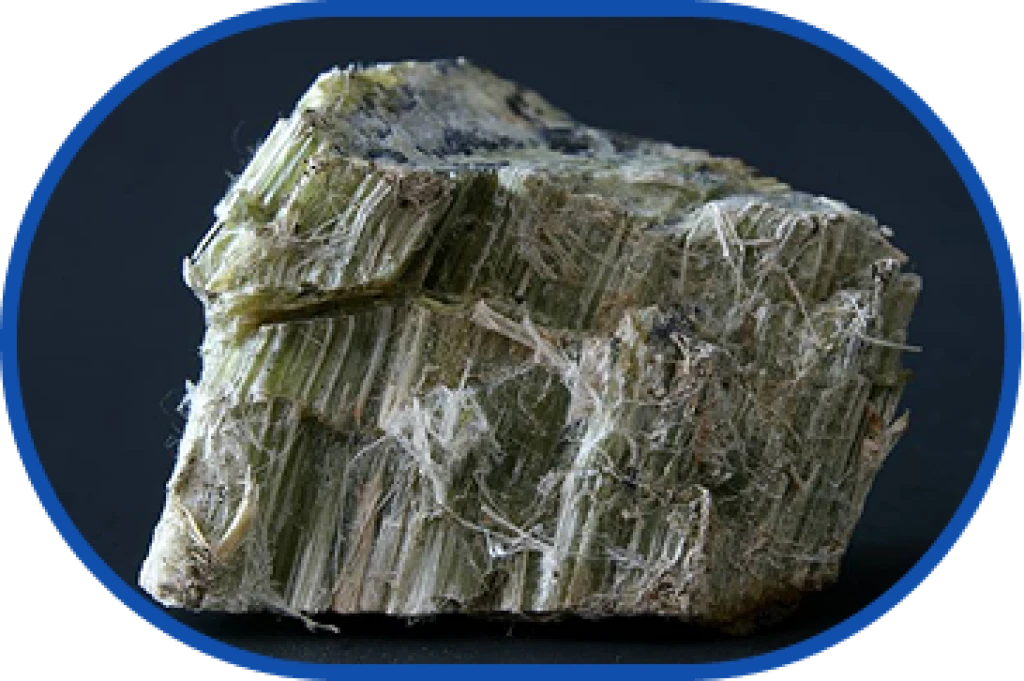

Experts distinguish two major groups of asbestos – amphibole and chrysotile. Numerous authoritative studies show that the amphibole group of asbestos poses the greatest risk to human health.





